What are Web Properties?
Web properties are very similar to regular properties with the addition that the value is retrieved from the client with each server call.
There are multiple ways this can be achieved, and which depends on the type of web property being used. There are three types of web properties:
What are Web Properties used for?
Web properties are used for configuring the UI, communicating the UI at the client, and storing data and application states.
Why are Web Properties needed?
These properties are the solution for a webapp server problem known as process pooling. This is when each call from the client to the server is potentially handled by a different process. The webapp server has no memory of any previous calls. It is essentially state-less. There is no persistency on the server, which means that if a value is set in a call it may not be retrieved again in a future call. Web Properties, using WebGet and WebSet, are the solution for this.
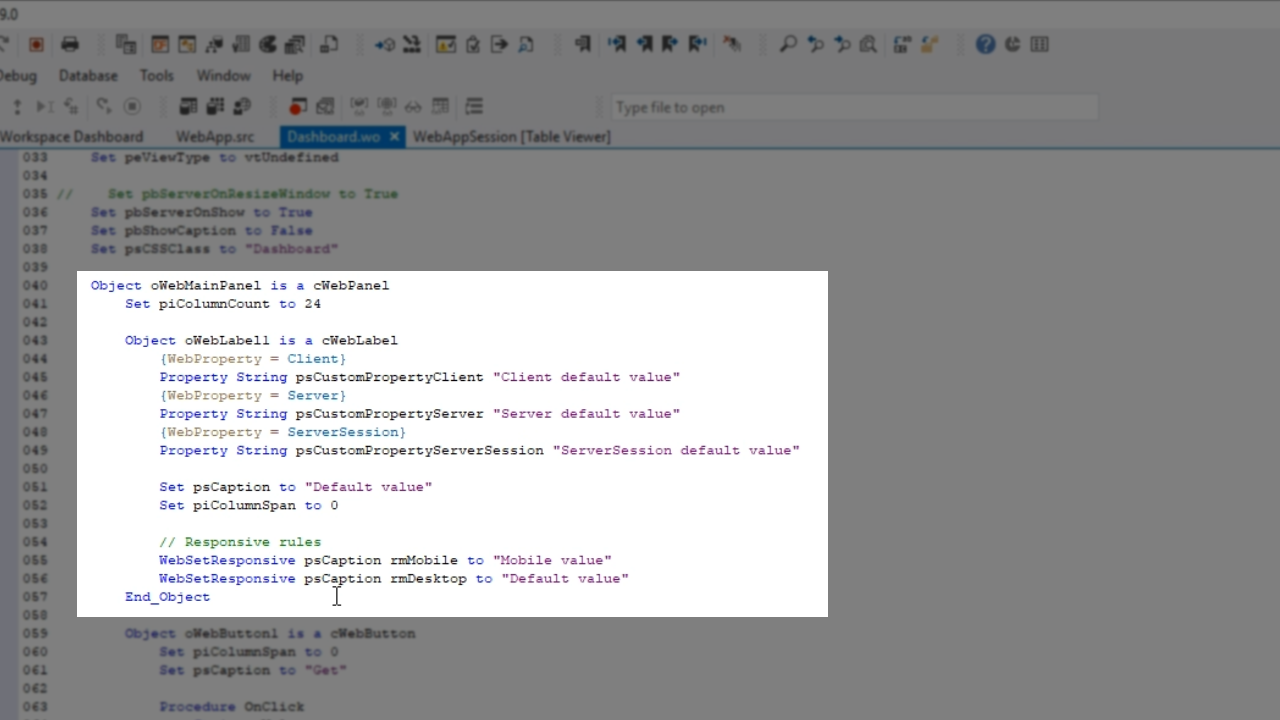
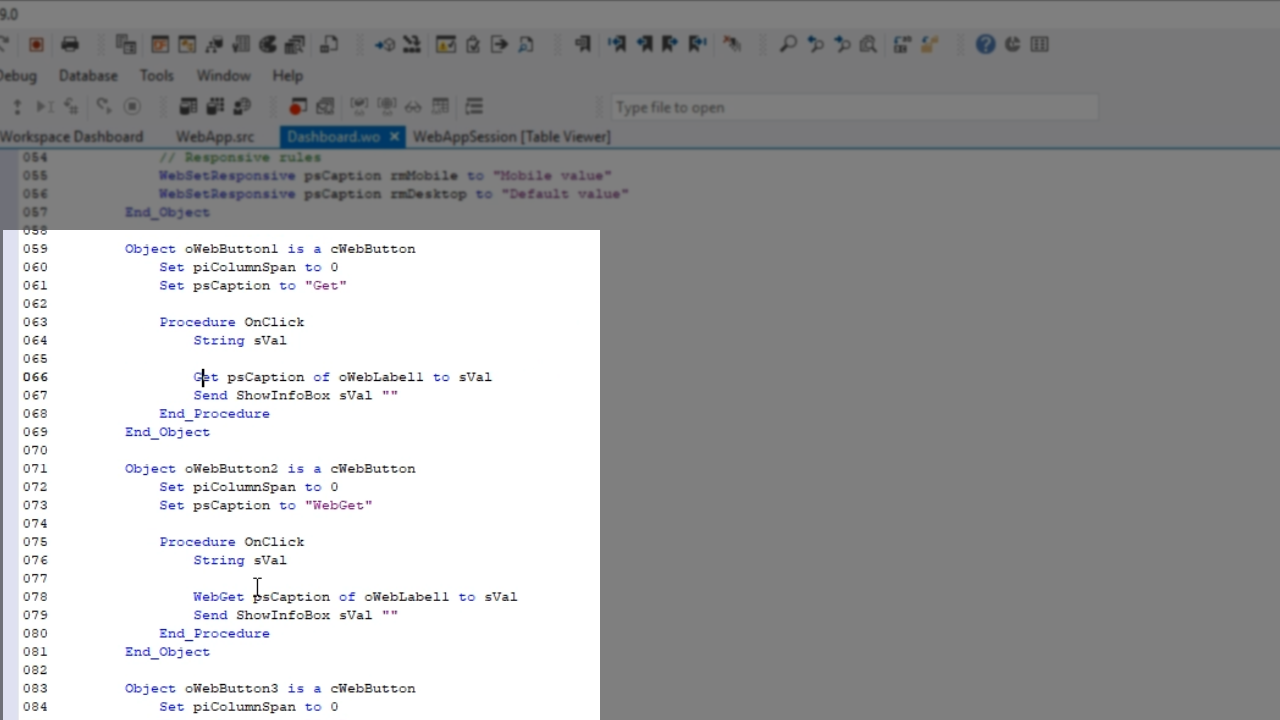
For any Web Property regular Get and Set calls can be used for the initial value up until the OnLoad event. If the value needs to be called or set at the runtime WebGet and WebSet are used.
Client Web Properties are slightly different. They are sent to the client upon WebApp initialization, and the first time the WebSet is used for the Client WebProperty it becomes synchronized. This means the value can be sent back-and-forth with each call.
Web properties also adhere to responsive rules. The value can be changed based on the current window size. This is done using WebSetResponsive. Several modes can be chosen to do this, but the most common modes are rmDesktop, rmTablet and rmMobile.
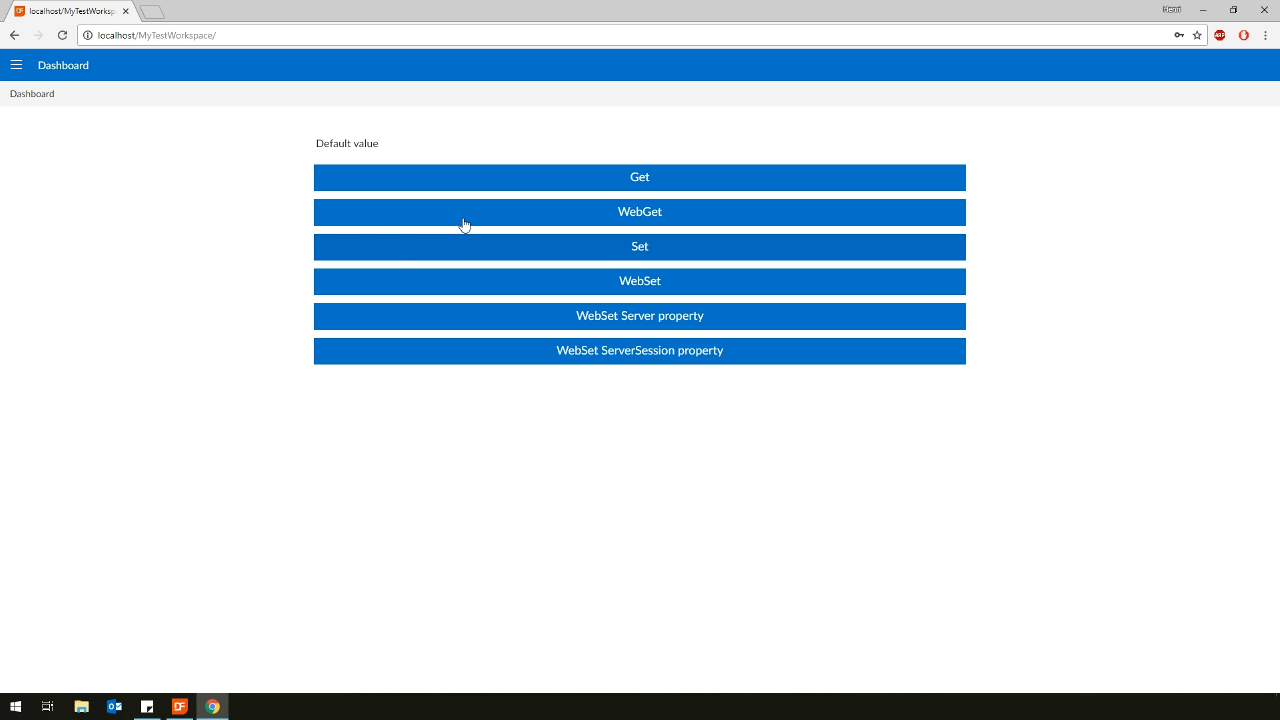
Demonstration